Calculation example – Elevation calculation and grade along a profile vertical curve
Contents [show]
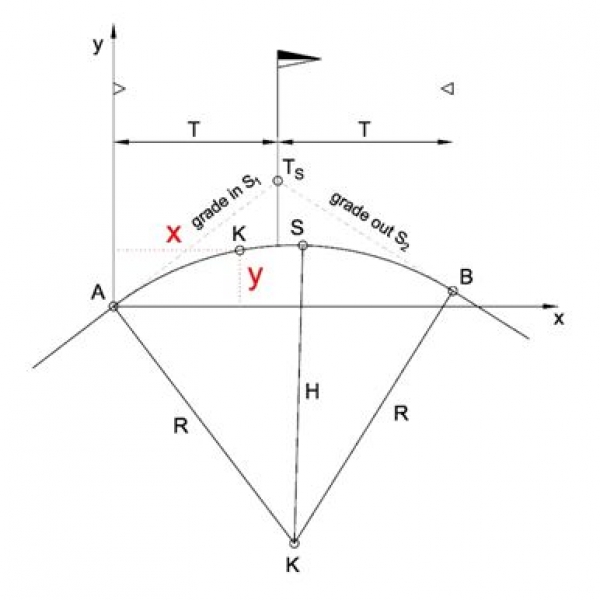
Determine the elevation and grade value of an unknown point K which lies along a profile vertical curve (convex in this example).
*Commonly in profile vertical curves, a parabola is applied as an approximation to circular curve, considering that for large radius values and target precision, these elements practically coincide.
Known values: Curvature radius H~R (positive for concave, negative for convex vertical curve), grade in S1 and grade out S2 (positive for ascending , negative for descending slopes), elevation of start point A of vertical curve HA
Solution: Elevation of point K at a distance x from curve start point A yK, grade value at point K SK
The vertical distance of point K from point A is calculated:
yK = (S1/100)*x + x2/(2*H)
The elevation of point K is calculated:
HK = HA + yK
Grade SK at point K calculation:
SK = S1 + (x/H)*100
Where:
S1 = grade in value at start point A of vertical curve
x = horizontal distance of point K from point A
H = curvature radius at peak of vertical curve (where grade s = 0%)
HA = elevation of start point A of vertical curve
Selected Topics
Want to read more like this?

Calculation example – Elevation Calculation along Profile Tangent
Sep, 22, 2017 | EducationDetermine the elevation of an unknown point X which lies between two known points A and B al...

Calculation example – Calculate the height of a building - 2
Mar, 19, 2019 | EducationCalculate the height of a building where the ground is sloping up or down from the observer. Know...
Calculation example - Calculate the height of an object when its top and bottom are visible but inaccessible
Jun, 26, 2019 | EducationCalculate the height of an object from a baseline when its top and bottom is visible but not accessi...

Calculation example - Resections
Oct, 18, 2019 | EducationCalculate the coordinates of a distant point Tn, referencing measured angles and coordinates of four...
Calculation example – Road design– Circular arc implementation
Sep, 22, 2017 | EducationHow to implement on the ground the main components (start, middle, end points) of a circular curve w...

Calculation example - Three Point Resection
Apr, 23, 2017 | EducationDetermine the coordinates of an unknown station P from three (3) previously coordinated reference po...

Calculation example – Road design– Circular arc implementation 2
Sep, 22, 2017 | EducationHow to implement on the ground the main components (start, middle, end points) of a circular curve w...

Calculation example - Calculate the height of an object when its top and bottom are visible but inaccessible #2
Oct, 18, 2019 | EducationCalculate the height of an object from a baseline when its top and bottom is visible but not accessi...

Calculation example – Calculate the height of a building
Sep, 22, 2017 | EducationCalculate the height of a building by observing its top from two ground points and measuring corresp...
Trending

Gauss's Area Calculation Formula
Walls at Alesia

Kallanai Dam (Grand Anicut)

Minoan Water Harvesting and Distribution (Terracotta Pipes)

Wall of Jericho

Calculation example – The intersection method

Ancient Greek Cisterns

