Understanding the Carola Bridge Collapse: Expert Insights


Sources: tu-dresden.de, physicalacoustics.com
Want to read more like this story?

Bridge Collapses in Bihar: A Wake-Up Call for Infrastructure Resilience
Aug, 13, 2024 | NewsIncreasing Incidents of Bridge Collapses in Extreme Weather The alarming frequency of bridge colla...

After the Recent NTSB Report: 68 U.S. Bridges Now Flagged for Collapse Risk
Mar, 29, 2025 | NewsWhen the Francis Scott Key Bridge in Baltimore catastrophically collapsed in March 2024 after being...

Lake Polyfytos Bridge in Greece is closed for at least a month due to structural damage
Mar, 16, 2023 | NewsThe Lake Polyfytos Bridge, in Greece, has been closed due to structural damage. More specifically...

Emphasis on Aesthetics Led to the Collapse of Tretten Timber Bridge in Norway
Aug, 15, 2022 | NewsFollowing the collapse of the Tretten Bridge in Norway in August 2022, an official report by the No...
An under-construction bridge in India has experienced its second collapse in a year: no fatalities
Jun, 08, 2023 | NewsThe collapse of a section of an under-construction bridge over the Ganges River has prompted an inv...

Florida pedestrian bridge collapses 5 days after its installation
Mar, 21, 2018 | NewsThe bridge, which was expected to open in January 2019, was being built using a method called a...

New bridge design offers high earthquake resistance at lower cost
Sep, 30, 2020 | NewsA new study focuses on the implementation of new bridge designs that could provide earthquake resist...
Norway wooden bridge collapse: Drivers of two vehicles rescued
Aug, 17, 2022 | NewsA wooden bridge over a river in southern Norway collapsed early Monday, with a car plunging into th...

Bridge Collapse in Peru: Structural Failure Sends Bus Crashing into River
Feb, 16, 2025 | NewsA tragic accident unfolded in northern Peru when a 60-meter-long bridge collapsed, sending a double...
Trending

Taipei 101’s impressive tuned mass damper

Characteristics of Load Bearing Masonry Construction

China Completes World’s Longest Expressway Tunnel, Redefining Connectivity
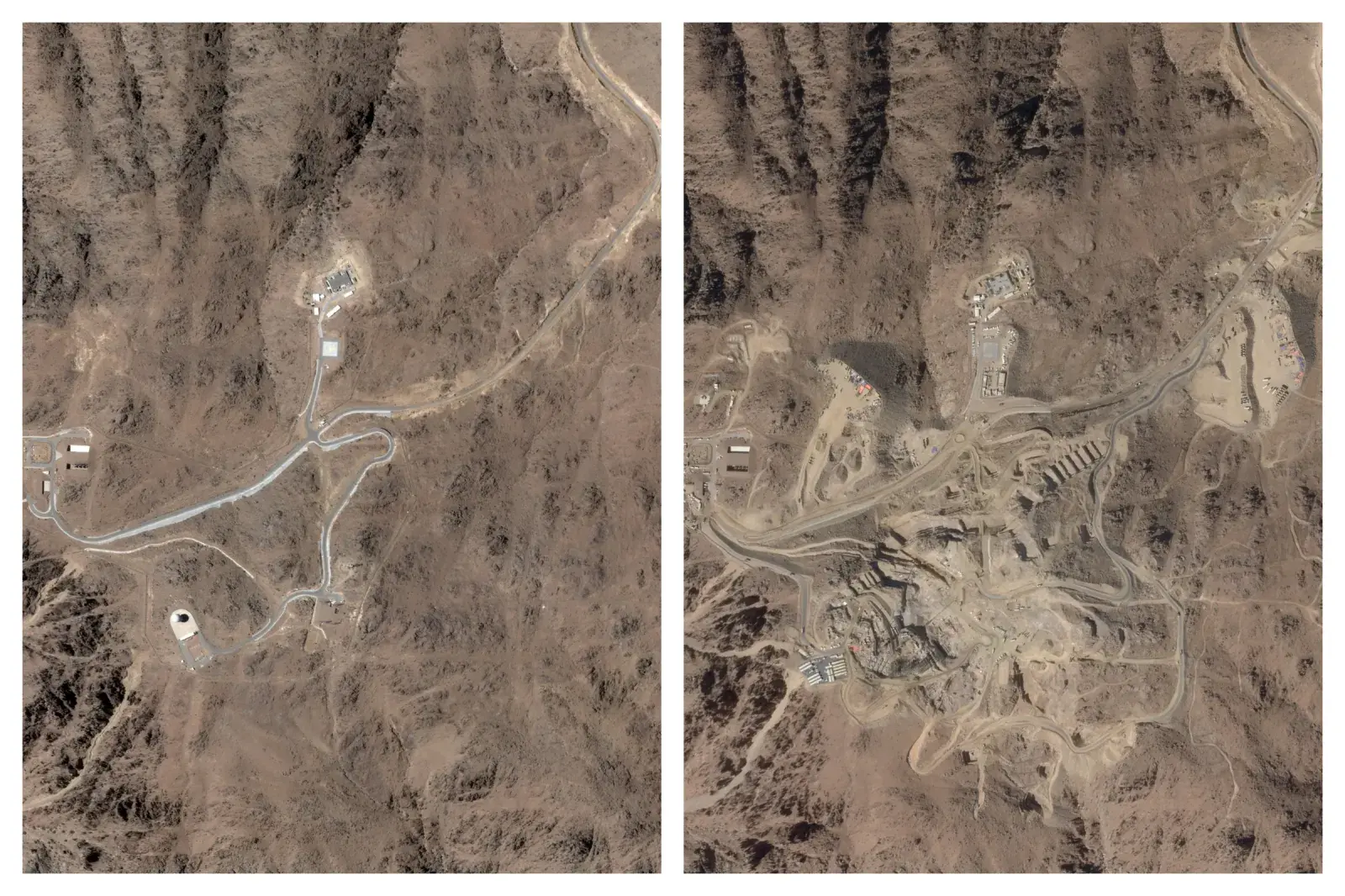

The Line at Neom faces feasibility reassessment while construction continues

The Billion-Dollar Airport Boom: 2025 Megaprojects Shaping the Skies

World's longest expressway tunnel to link northern and southern Xinjiang