The Devastating Floods in Valencia: A Call for Enhanced Engineering Solutions



Sources: newcivilengineer.com, cbsnews.com, bbc.com
Want to read more like this story?

The Devastating Impact and Solutions to Flooding in Brazil
May, 20, 2024 | NewsThe recent catastrophic flooding in Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil, has brought widespread devastation a...

Dubai’s $8B Flood Defense Plan: Engineering a Resilient Future
Jul, 12, 2024 | NewsExpanding Capacity with Traditional Approaches In response to April’s unprecedented storm that inu...

Dam Collapse in Sudan: Catastrophic Flooding Leaves 30 Dead, 150 Missing
Aug, 27, 2024 | NewsA tragic incident has unfolded in Arbaat, Sudan, on August 27th, where the collapse of a dam has le...

£200M Leeds Flood Scheme Safeguards Homes, Businesses, and Biodiversity
Nov, 26, 2024 | NewsThe Leeds Flood Alleviation Scheme is a landmark £200 million project aimed at protecting over 4,0...
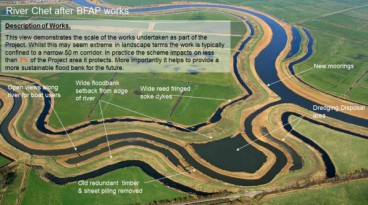
Major flood defense project in UK completed
Sep, 01, 2021 | NewsA project that lasted for 20 years and aims at defending a vulnerable region to flooding in the UK h...
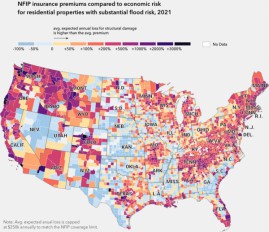
Flood risk increase for US infrastructure due to climate change: Insurance rates tend to underestimate the current conditions
Mar, 01, 2021 | NewsThe risk of flooding can cause severe damage to infrastructure. New evidence revealed that the poten...

Flood Waters in Nepal Break Through Defense Wall (Video)
Aug, 09, 2016 | NewsHeavy rainfall in Nepal continues and mass flooding is causing severe damage. Flash flooding and lan...

Wisconsin engineers create flood risk prediction tool for Lower Mississippi River Basin
Oct, 17, 2025 | NewsResearchers at the University of Wisconsin have introduced a new computer model designed to predict...

New satellite mission will enable better flood prediction modeling
Sep, 30, 2019 | NewsAccording to a recent study, a new satellite, set to launch in 2021, will offer a better understandi...
Trending

Taipei 101’s impressive tuned mass damper

Characteristics of Load Bearing Masonry Construction

The Billion-Dollar Airport Boom: 2025 Megaprojects Shaping the Skies

China Completes World’s Longest Expressway Tunnel, Redefining Connectivity

Dutch greenhouses have revolutionized modern farming



