Calculation example – Elevation calculation and grade along a profile vertical curve
Contents [show]
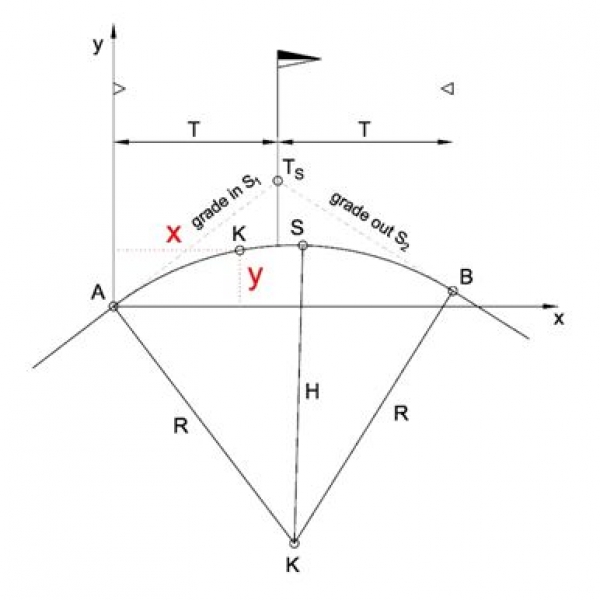
Determine the elevation and grade value of an unknown point K which lies along a profile vertical curve (convex in this example).
*Commonly in profile vertical curves, a parabola is applied as an approximation to circular curve, considering that for large radius values and target precision, these elements practically coincide.
Known values: Curvature radius H~R (positive for concave, negative for convex vertical curve), grade in S1 and grade out S2 (positive for ascending , negative for descending slopes), elevation of start point A of vertical curve HA
Solution: Elevation of point K at a distance x from curve start point A yK, grade value at point K SK
The vertical distance of point K from point A is calculated:
yK = (S1/100)*x + x2/(2*H)
The elevation of point K is calculated:
HK = HA + yK
Grade SK at point K calculation:
SK = S1 + (x/H)*100
Where:
S1 = grade in value at start point A of vertical curve
x = horizontal distance of point K from point A
H = curvature radius at peak of vertical curve (where grade s = 0%)
HA = elevation of start point A of vertical curve
Selected Topics
See Also

The history of the Golden Gate Bridge
Nov, 24, 2023The Golden Gate Bridge opened on May 27, 193...
Professional Examinations Preparation
Jun, 08, 2022
Calculation Examples
Jun, 08, 2022

Calculation example - Find the bearing of an apparent dip (two symmetrical to full dip directions), given the rate and direction of full dip
Nov, 30, 2020Given the rate and direction of full dip of a pla...
Calculation example - Find path gradients in different directions, given the rate and direction of full dip
Nov, 20, 2020Given the rate and direction of full dip of a plan...







