This inflatable solar collector constitutes a low cost CSP plant with significant carbon reductions

It allows 55% cost savings and a 40% CO2 reduction compared to the best future parabolic trough technologies
It allows 55% cost savings and a 40% CO2 reduction compared to the best future parabolic trough technologies
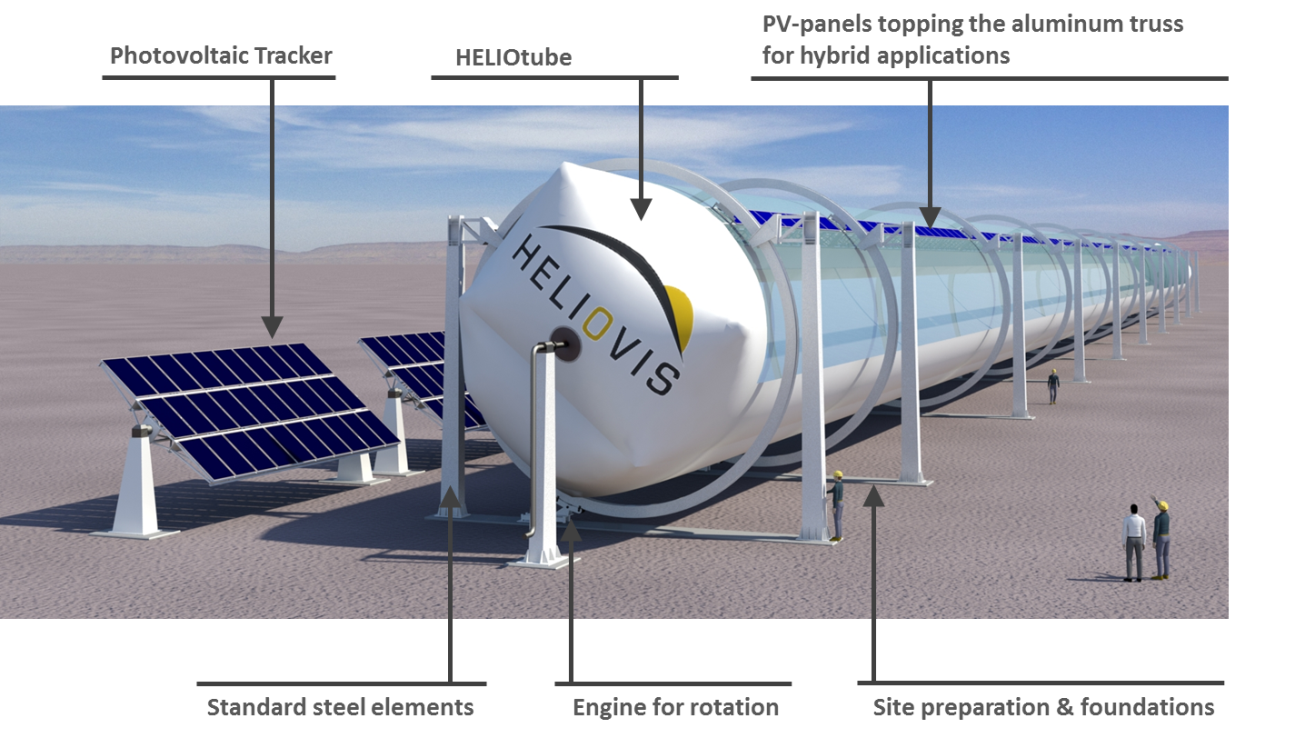
The Austrian company HELIOVIS AG has developed HELIOtube, an inflatable solar collector that is considered to be cheaper (by 55%) and less resource and energy intensive in comparison to conventional technologies (parabolic troughs, Towers, Linear Fresnels, Parabolic Dishes). Another benefit is that is has a lower carbon footprint, as it achieves a 40% CO2 reduction compared to the best future parabolic trough technologies.
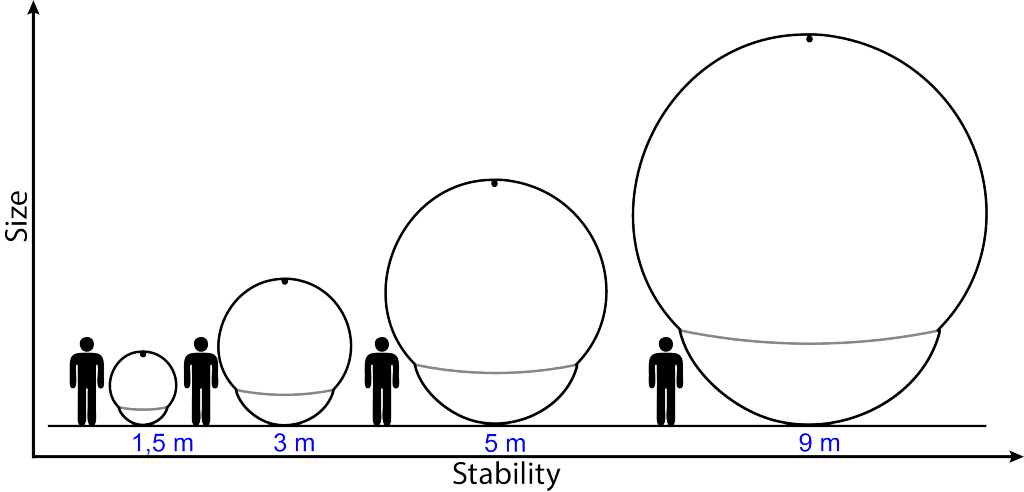
This concentrated solar power plant (CSP) is made of commercially available recyclable plastic films (instead of the current steel-and-glass based technologies) and in full scale is 220m long and 9m in diameter. Yet, it can be transported while rolled in a standard container (simple logistics) and be inflated at the site designated for the power plant, offering significant competitive advantages in terms of required materials and production, logistics, and installation costs. Another competitive advantage it has is that when it comes to larger dimensions, conventional systems face difficulties on construction design and stability. On the contrary, the larger the HELIOtube’s diameter, the smaller the pressure that is required to stretch the films and the more stable the entire construction design becomes.
How it works
The HELIOtube is aligned from North to South and tracks the sun one-dimensionally from East to West. It is equipped with a mirror film that divides the cylinder into two air-tight chambers running lengthwise through the tube. There is a small pressure difference between the top and bottom chambers that arches the mirror film downward, so a mirror channel is created. There, the incident solar radiation is concentrated onto a focus line in the upper chamber and heats the thermal receiver fluid to a temperature of 400 to 600° C, enough to provide steam to turbines for electricity generation.
Currently, HELIOVIS AG is collaborating with the German company MachtWissen in order to design, deploy and run a large scale pilot in Spain, before the product is ready for commercialization. In-field test of transport and installation logistic operations will also be run. HELIOtube will span 2 years with a budget of 2.5 million euro, out of which 1.8 million will be funded by EU’s HORIZON 2020 program.

Want to read more like this story?

2016 was a milestone for large-scale solar energy projects in Australia
May, 15, 2017 | NewsWind power has also gained ground in the country as its cost has fallen Wind power has also gaine...

World-first commercial carbon-capture plant opens in Switzerland
Jul, 10, 2017 | NewsIts aim is to capture 1% of global CO2 emissions by 2025 Its aim is to capture 1% of global CO2 emi...

World’s largest single-tower solar thermal power plant to be built in South Australia
Sep, 14, 2017 | NewsThe massive AUD $650 million installation will have a proposed output of 150 MW The massive AUD $65...

Energy storage could take renewable technology to a whole new level …
Jul, 04, 2016 | NewsStorage systems can make economic sense for renewable energy sources such as wind and solar, accordi...

Huge Solar Thermal Power Plant In Morocco
Nov, 25, 2015 | NewsA huge plant at Ouarzazate, Morocco using energy from the Sun is expected to open next month. A h...

World's tallest Solar Tower under construction in Israel
Feb, 25, 2016 | NewsThe project is called Ashalim and the solar tower will be 240m (787ft) tall The project is called...

Drones may help in designing future solar farms
Apr, 18, 2017 | NewsThey can get the job done more quickly and efficiently, while reducing the costs involved They ca...

How about space-based solar panels?
Apr, 19, 2018 | NewsThe concept was theorized over half a decade ago, as space-based solar arrays would be illuminated 2...
The prospects for carbon-neutral buildings
Oct, 27, 2023 | NewsIn the United Kingdom, buildings account for 33% of greenhouse gas emissions and 40% of global ener...
Trending

Vertical gardens in Mexico City to combat pollution

Saudi Park Closed After 360 Big Pendulum Ride Crashes to Ground, 23 injured

Characteristics of Load Bearing Masonry Construction

Taipei 101’s impressive tuned mass damper

Dutch greenhouses have revolutionized modern farming

Federal court rules Biden’s offshore drilling ban unlawful


