Next generation of smart homes

The new era of smart houses is whar researchers call the "Internet of Ears''.
The present technology of smart homes features multiple systems that can interact using the Internet. From manipulating common appliances to regulating heating system from a remote area, the applications of the “Internet of Things (IoT)” is growing rapidly.
At the same time, 2 researchers, Ming-Chun Huang and Soumyajit Mandal, both Assistant Professors of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science in Case Western Reserve University are experimenting on a different system. Their method utilizes new sensors that will be able to perceive sounds, vibrations, movements and even alterations in the electrical field of a house. These sensors could be placed in the walls and floor will be able to capture someone's activity. “We are using principles similar to those of the human ear, where vibrations are picked up and our algorithms decipher them to determine your specific movements. That’s why we call it the ‘Internet of Ears,” Prof. Huang stated while he admits that this technology is about a decade away.
Prof. Mandal explains how the sensors can manipulate the electrical field of a room in order to perceive the presense of people. “There is actually a constant 60 Hz electrical field all around us, and because people are somewhat conductive, they short out the field just a little. So, by measuring the disturbance in that field, we are able to determine their presence, or even their breathing, even when there are no vibrations associated with sound,” he said.
The researchers elaborated about the benefits of the method that they suggest. First of all, the sensors will provide the ability to measure a building's human occupancy which will be critical in cases of emergencies like hurricanes or severe earthquakes. “This hasn’t really been explored as far as we’ve seen, but we know that humans create a dynamic load on buildings, especially in older buildings. In collaboration with our colleague YeongAe Heo in Civil Engineering , we are trying to predict if there is going to be structural damage because of the increased weight or load based on the number of people on the floor or how they are distributed on that floor,” Prof. Huand stated. Moreover, houses will be more energy efficient as the elecrtical and heating systems will adjust to the location of the humans at a given time.
Sources: Thedaily.case.edu, Marketbusinessnews.com
Sources: Thedaily.case.edu, Marketbusinessnews.com
Want to read more like this story?
Smart buildings potential and limitations
Nov, 25, 2019 | NewsSmart buildings have the capability of completely changing the future of building infrastructure. Ho...

The Internet of Things in building industry
Aug, 01, 2021 | NewsThe Internet of Things (IoT) is currently developed and can be applied to the building industry gene...
Seismic isolation: engineers launch a new building system to protect houses in an earthquake
Oct, 25, 2022 | NewsA University of Canterbury team, led by Civil and Natural Resources Engineering Professor Tim Sulli...
Changes in magnetic field along fault lines preceded major earthquakes in California according to a recent case-study
Oct, 20, 2022 | NewsResearchers have tried for decades to determine whether there is a reliable precursor that can act...
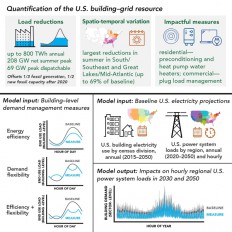
Control building energy demand to preserve the electrical power resources
Jul, 07, 2021 | NewsA new study conducted in the United States quantifies how the optimization of the consumed energy in...

Best ways to reduce energy consumption in buildings
Apr, 14, 2016 | NewsPractices with greatest impact on energy conservation are under study Practices with greatest imp...

Researchers have developed a miniaturized water quality sensor that can monitor drinking water quality in real time
Oct, 03, 2017 | NewsThis tiny and inexpensive device -built using a 3D printer- can be deployed anywhere in the water di...

Smart technology in road infrastructure
Nov, 25, 2019 | NewsA new project, currently conducted in the United Kingdom, aims to produce energy from traffic, compl...
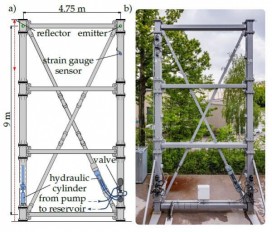
New technique to monitor structural deformation in real time
Mar, 16, 2020 | NewsScientists have developed a new, low-cost method to detect and precisely measure the deformation of...
Trending

Vertical gardens in Mexico City to combat pollution

Saudi Park Closed After 360 Big Pendulum Ride Crashes to Ground, 23 injured

Characteristics of Load Bearing Masonry Construction

Taipei 101’s impressive tuned mass damper

Dutch greenhouses have revolutionized modern farming

Federal court rules Biden’s offshore drilling ban unlawful


