2024 ice tsunami in Yukon River tore through forest, altered riverbed
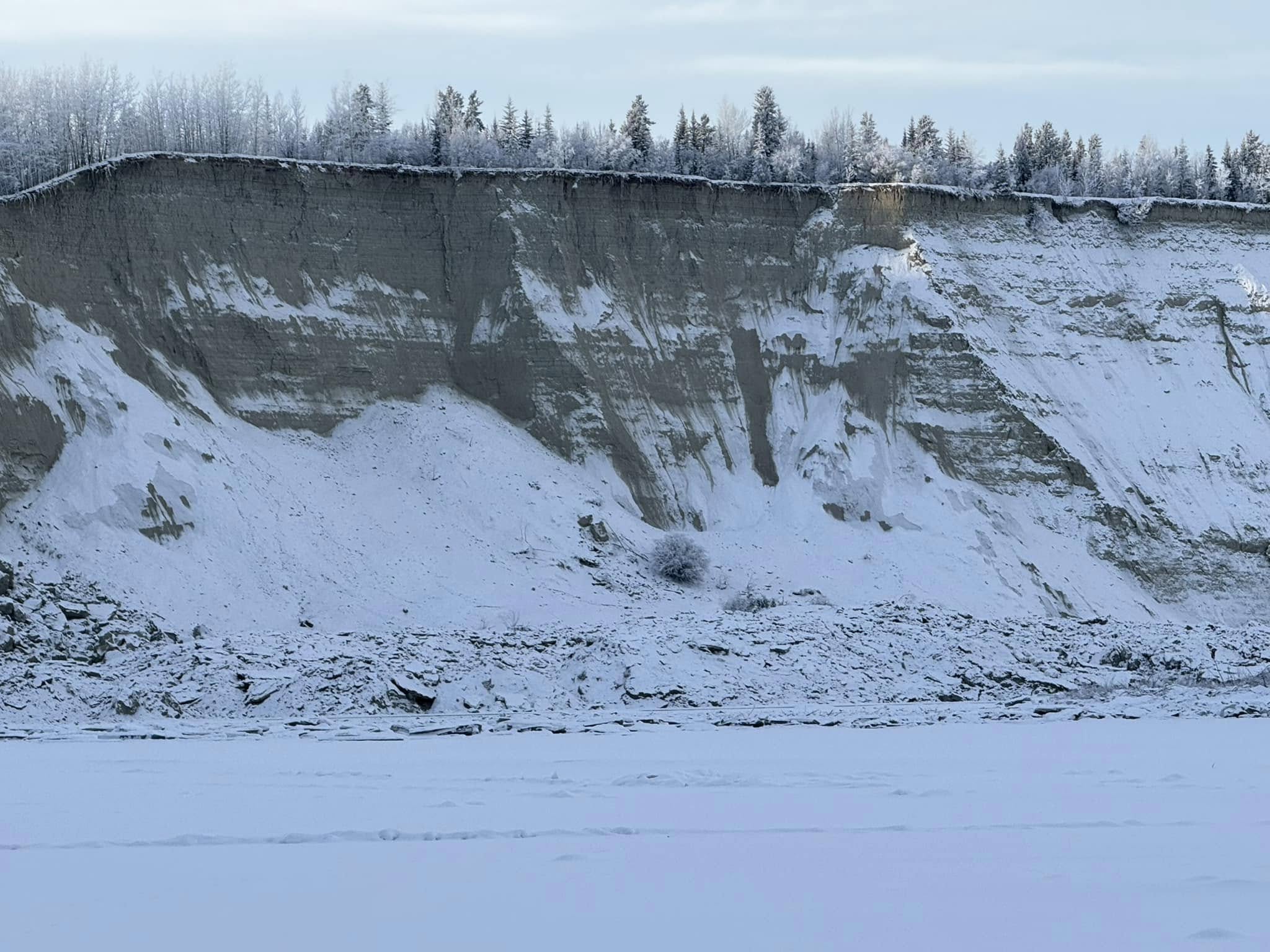

In 2024, an extraordinary ice-driven flood, termed an “ice tsunami”, raced along the Yukon River with such intensity that it uprooted hundreds of trees and stripped sediment from the riverbed. The event occurred during a cold season when thick ice cover suddenly broke apart, sending massive sheets downstream at high velocity.
Satellite imagery and on-site surveys reveal zones where fast-moving ice slabs gouged into riverbanks, removing both soil and rooted vegetation and leaving deep scours along the channel edge. In certain reaches, up to 10 meters of riverbank collapse was documented, along with terraces of exposed bedrock previously hidden under sediment.
Researchers describe this as more than a typical spring breakup; the sudden and forceful breakup propagated as a wave of ice fragments that acted like solid projectiles, capable of exerting dynamic pressure comparable to flood currents. Unlike normal ice jams or gradual thawing, this event initiated a shock wave effect, ice fragments collided and conveyed energy downstream, amplifying destructive potential.
Ecological consequences were severe. Uprooted trees fell into the river, altering flow patterns and creating debris jams. Riverine habitats that supported riparian vegetation and fish spawning grounds were disrupted by channel shifts and disturbance to substrate layers. Sediment mobilized by the event was transported far downstream and deposited in new configurations, changing local bed morphology.
Source: Live Science
Want to read more like this story?

NASA flies over the poles to monitor ice loss
Jun, 22, 2017 | NewsSea ice in the Arctic reached the lowest maximum wintertime extent ever recorded Sea ice in the Arc...

Arctic Sea Ice Hits Record Low
Feb, 15, 2015 | NewsAccording to data from the NASA-supported National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC) at the Universit...

The Largest Ice Shelf In Antarctica Melting
Jul, 06, 2015 | NewsScientists warn that the global warming may cause the detachment of the largest ice shelf in Antarct...

The ‘ice stupas’ could solve the water crisis in the high desert of the Himalayas
Jun, 15, 2018 | NewsArtificial glaciers are used to store the flowing winter water -that otherwise is wasted down the st...

Hazard of landslide-triggered tsunamis due to glaciers melting
Sep, 14, 2018 | NewsA new study shows that landslides, on slopes where ice retreats, can trigger massive tsunamis. A ne...

Geoengineering West Antarctic glacier to prevent a 3-meter sea level rise
Jul, 29, 2019 | NewsA group of scientists suggests a revolutionary strategy to prevent the collapse of the west Antarct...

Greenland's thick ice slabs may cause sea level to rise
Oct, 02, 2019 | NewsSea level may rise by 10 centimeters due to the presence of thick ice slabs in Greenland. A new stu...

Dortmund’s Visionary ICE Plant: Merging Technology and Sustainability in Rail
Dec, 03, 2024 | NewsThe construction of a cutting-edge maintenance facility in Dortmund is set to redefine rail infrast...
Hidden Flows Could Be Behind Antarctic Melt
Mar, 16, 2015 | NewsTwo previously unnoticed oceanic gateways of warm water have been linked to the extreme thinning of...
Trending

Vertical gardens in Mexico City to combat pollution

Saudi Park Closed After 360 Big Pendulum Ride Crashes to Ground, 23 injured

Characteristics of Load Bearing Masonry Construction

Taipei 101’s impressive tuned mass damper

Dutch greenhouses have revolutionized modern farming

Federal court rules Biden’s offshore drilling ban unlawful


